What is website audit- Mastering SEO Audits and Website Audits for Exceptional Online Performance
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) audits serve as the foundation for improving website performance and visibility in search engines. your goal is to improve search engine rankings, attract more organic traffic, or understand user behavior, an SEO audit is your gateway to achieving these objectives.
An SEO audit is a structured evaluation of a website to assess how well it adheres to search engine optimization best practices. This process focuses on a variety of aspects, including:
Technical functionalities like crawling, indexing, and page speed.
- On-page elements, such as metadata and keywords.
- Off-page factors involving backlinks and domain authority.
- Content quality in terms of relevance, structure, and engagement.
- User experience (UX), which determines ease of access and satisfaction.
- Mobile-friendliness, ensuring seamless browsing across devices.
An SEO audit generates actionable insights for identifying weaknesses that are preventing optimal performance. By understanding these weak spots, you’ll be able to apply targeted strategies that enhance search engine rankings, boost site traffic, and foster prolonged audience engagement.
Why Is an SEO Audit Important
Your website is your primary digital asset— it has the power to influence how people and search engines perceive your brand. Without regular auditing, small technical issues or obsolete strategies might act as unnoticeable barriers that derail your progress. Here’s why undertaking an SEO audit is critical to your online success:
1. Pinpoint Technical Problems: Your website might seem functional from a user’s perspective, yet search engines may face challenges crawling and indexing it. Technical errors like server issues, broken internal links, or misplaced redirects hinder accessibility and cause a decline in rankings.
2. Adapt to Algorithm Updates : Search engine algorithms, particularly Google’s, are constantly evolving. Conducting an SEO audit on a regular basis ensures your site complies with the latest updates and avoids penalties that come from outdated practices.
3. Enhance User Experience (UX) : Website performance is often judged by how user-friendly it is. Slow load speeds, confusing navigation, and fixes like broken images can repel visitors. An SEO audit evaluates and improves these areas, giving your audience a smooth experience.
4. Benchmark Performance : An SEO audit provides measurable benchmarks for success. By tracking metrics such as organic traffic, bounce rate, or keyword rankings, site owners can instantly measure the impact of optimization efforts.
5. Stay Ahead of the Competition : No matter your industry, standing out is vital. SEO auditing helps analyze competitor weaknesses, uncovering opportunities to secure your competitive edge and redefine your niche. Now that we understand the "why," let's break down exactly what makes up an SEO audit.
Essential Pillars of a Website Audit
- Technical SEO Audit
- On-Page SEO Audit
- Off-Page SEO Analysis
- Content Quality Assessment
- User Experience (UX)
- User Experience (UX)
1. Technical SEO Audit
It is the practice of optimizing a website and its infrastructure to improve search engine visibility and the user experience.
It helps search engine spiders:
- Crawl
- Index
- Rank
To enhance website ranking organically:
• Optimize the website's architecture
• Add internal linking
• Fix any errors that may be preventing the site from ranking higher
Search engines prefer websites with technical qualities such as :
Ensures that websites are technically optimized and kept up-to-date with search engine algorithms because they:
• Change often
• Add new features
• Update algorithms frequently
If the website is not optimized technically, it impacts ranking
Factors in Technical SEO
- Page load time
- Mobile friendliness
- Sitemap
- Site security
- Duplicate content
- Structured data markups (Schema)
Web Crawlers
They are internet bots that systematically browse the World Wide Web. It helps in :
• Downloading and indexing content from websites
• Scanning the internet and identifying pertinent links
• Classifying and organizing the issues according to their relevance
They are also known as search engine bots or spiders.
Mechanism of Web Crawlers
It starts from the seed or different types of known URLs.
They crawl the web pages and find hyperlinks to other URLs,which are added to the list of pages to be crawled next.
They decide which page to crawl based on the robots.txt protocol.
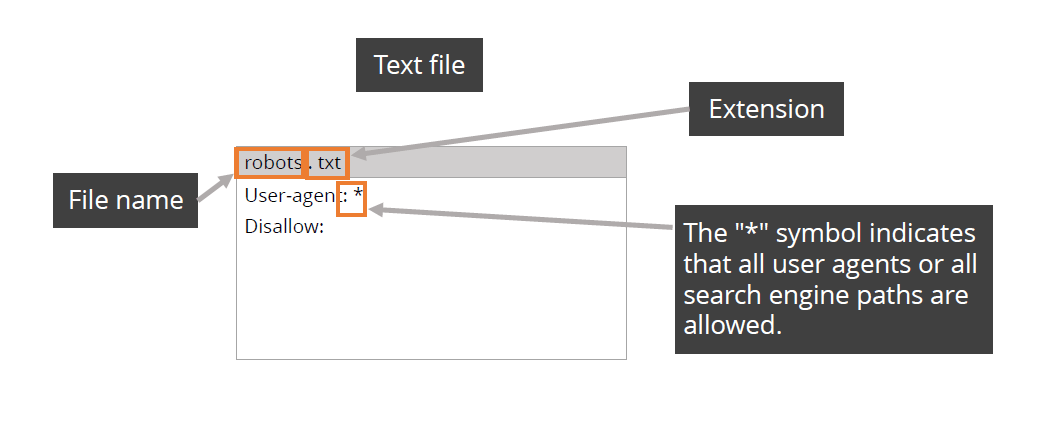
Robots.txt file has specific protocols for bots accessing the host website or application. It is a text file placed in the root directory of a website to instruct crawlers.
Indexing
It is the process of analyzing and storing the information from the websites by search engine bot.
• Pages not indexed by bots do not appear on search engine result pages (SERPs).
• Indexing makes websites more visible to the audience.
The first step to increasewebsite traffic, sales, andconversions for a companyis Google indexing.
Ranking
It is a website feature that search engine algorithms examine while determining its ranking. Some of the ranking variables are:
• Content
• Links
• Mobile SEO
• UX
Key Technical Elements to Review
• Site Crawlability: search engines capable of navigating and assessing your website. Examine the robots.txt file, eliminate crawl blocks, and utilize tools like Google Search Console for an overview.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a protocol that exists at the domain level as an individual text file. It provides:
• Instructions to the search engines regarding what to index and what not to.
• A set of instructions about what content to exclude from indexing.
The robots.txt file can be used:
• To block sites in development from getting indexed and published in the search engines before they are completely ready
• To exclude landing pages from paid campaigns
Robots.txt is only a protocol and not a security measure; not every bot or search engine will follow the instructions provided.
Robots.txt Examples
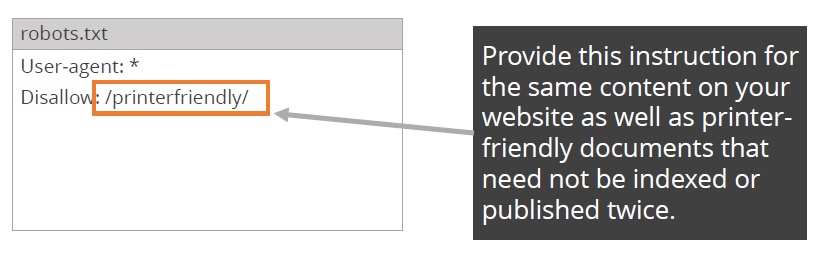
The example shows how instructions are given to search engines not to index the directory of printer friendly documents.
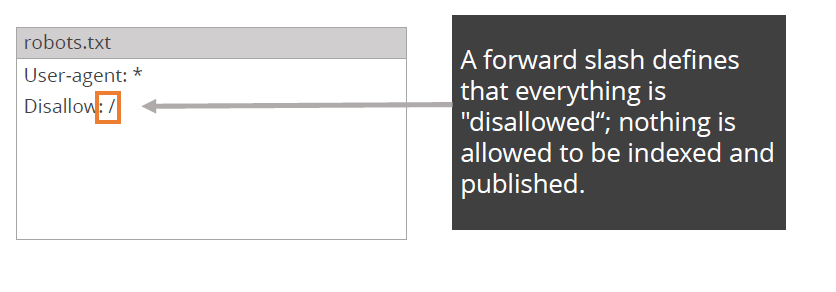
The example shows what instructions you can give to the search engines if you want to block all access to your website.
Most of the times websites don’t show in search engine due to wrongly configured robots.txt file. It is important to understand, manage, and update your robots.txt file correctly to ensure that your website is indexed and published correctly by search engines.
The hreflang Tag
The hreflang tag indicates to the search engines the language used on the web page.
• It specifies the audience for the web page.
• It notifies the search engines about multiple versions of the same content, that is, content that has been translated into
different languages.
• It avoids duplicated content that has been indexed and published by search engines.
• It provides regional variations of a single language targeted at different regions, for example, English language content for UK, US, and Australia.
The hreflang tags can be placed in the header section within the page using the HTTP protocol, or in the sitemap.
The proper format of the hreflang tag is: Rel=“alternate” hreflang=“language”
(It specifies that the webpage is a translated version of another web page.)
Language values can be used with the hreflang tag.
hreflang=“enUS” tag specifies that the webpage displays English content for US users.
hreflang=“enGB” tag specifies that the webpage displays English content for UK users.
URL Structure
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is the address or document on the internet. Every web page has its own address and a domain name that appears at the root level of the URL. The URL keeps building as you click additional pages, as there is a subdirectory, a product directory, and additional details.
Rewriting URLs
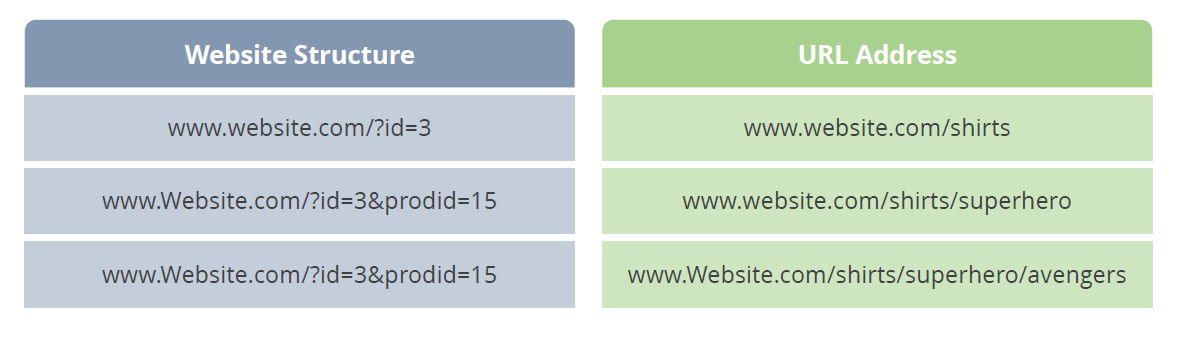
You also have to understand the process of building the database to recreate a pattern, in order to recreate a user friendly URL. If your site ranks well and gets a lot of visitors from search engines, then the URL need not be restructured or rewritten.
URL Redirect
Redirect involves forwarding/redirecting the request to a new page/URL. It includes:
• Change of URL
• Change of index page location from root
• Change of pages within a domain send to new URL (301,302)
There are two types of URL redirects
301
- Permanent Redirect
- Preferred method to redirect all pages to new destinations as the value of the link going to the Alt page is applied to the new page.
302
- Temporary Redirect
- The value of the link does not pass from the Alt page to the new page as it is a temporary redirect and will be replaced.
Canonicalization
Canonicalization refers to redirecting to a single website from multiple URLs.
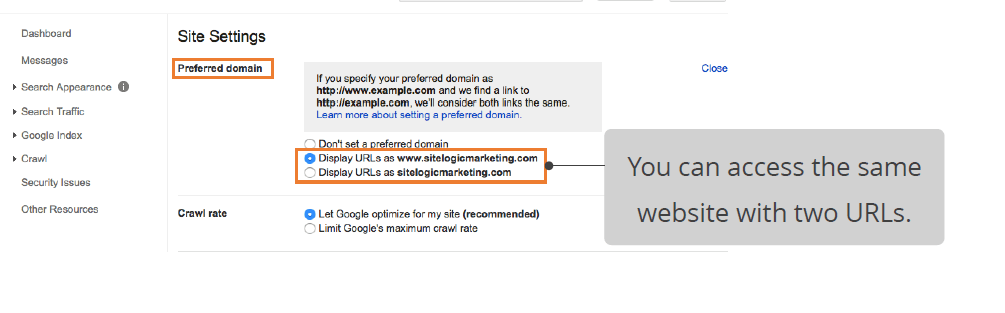
Canonicalization poses a threat, as the same homepage can be accessedthrough two different addresses. Canonicalization leads to duplication of content as the same page is published under multiple URLs.
How to Identify Duplicate Content
Method 1 is a simple method :
• Copy a paragraph of content from your website.
• Paste it in the search engine with quote sand tap the search icon.
• Observe how many of the same pages of your website appear in the results indifferent URLs.
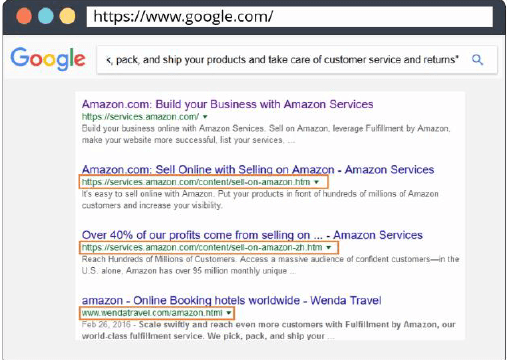
Method 2 is slightly complex
Use the SEO management software program to perform an indepth investigation about your website duplicity.
The SEO management software program spiders your website and manages the duplicate content of your website.
You can also utilize thirdparty services to spider your website and ensure that no duplicate content is available for your website
Sitemaps
A sitemap is:
•An index of all the content pages, posts, authors, images,and information on the website.
•A direct map containing direct links to all the files that canbe provided to search engines.
•A directory containing the addresses of all the pages of the website.
•A clear index of content for search engines and helps large websites, such as ecommerce sites, with a huge directory of products.
You can submit a sitemap through webmaster tools.
Site maps Important Points
- Sitemaps make the job easier for search engines by providing direct links to web pages.
- Search engines prefer to find websites through natural crawling and indexing.
- Natural indexing by search engines enables additional context of your website byevaluating linking, citation, and surrounding communities that link to that website.
- Creating a sitemap does not affect site rankings.Creating
- Creating a sitemap is optional. Not creating one won't harm your site.
Page Load Time
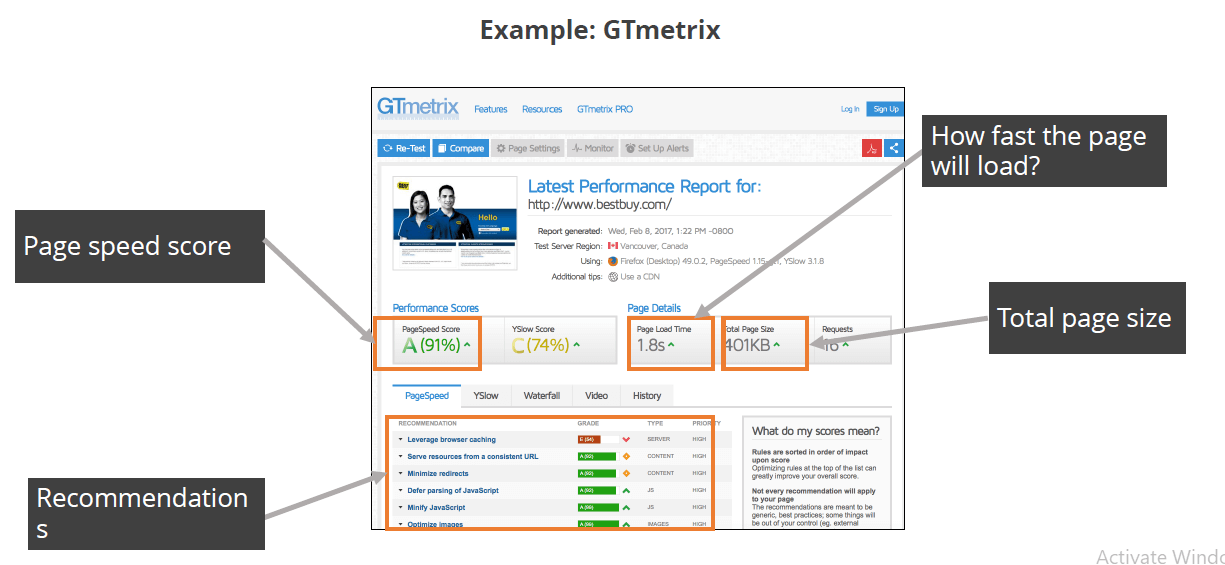
Search engines are very particular about the page load time and consider it as a quality indicator.
When a page is fast, it is lighter, takes less space, and also provides a better user experience. Use third party tools that can provide reports on how fast your web page loads.Example: GTmetrix
Tools for Technical SEO Audits:
• Screaming Frog SEO Spider for identifying crawl issues.
• Google Page Speed Insights to test page load times.
• Ahrefs Webmaster Tools for diagnosing broken links.
2. On-Page SEO Audit
On-page SEO elements involve internal optimizations that influence how well individual pages rank. These consist of keywords, HTML elements, image optimization, and more.
Checkpoints for On-Page:
Title Tags & Meta Descriptions: Title Tags & Meta Descriptions: These should be relevant, compelling, and no longer than 60 characters for titles or 160 for meta descriptions.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Organize page content into digestible chunks using proper headers.
Keyword Integration: Use target keywords naturally in the body text, headings, and anchor text. Excessive keyword "stuffing" is counterproductive.
Image Optimization: Include relevant alt text, compress images to reduce file size, and pick descriptive file names.
Step-by-Step Optimization:
1. Audit metadata and replace missing descriptions.
2. Revisit blog titles and use focus keywords up front.
3. Compress media to ensure faster load speeds without sacrificing quality.
While technical SEO improves accessibility, on-page SEO establishes content relevance, making it easier for engines to align your pages with user intent.
3. Off-Page SEO Analysis
Off-page SEO refers to actions that occur beyond your website but directly impact its authority and visibility.
Core Components:
- Backlinks: Look for authoritative websites linking back to your domain. Links from reputable sources like The New York Times hold more value than spammy blogs.
- Domain Authority (DA): Build your credibility by maintaining a strong off-site presence and publishing high-value content.
- Social Media Presence: Engage users through social shares, comments, and mentions on major platforms.
Tools to Monitor Off-Page Efforts:
• Ahrefs and Moz Link Explorer to evaluate backlink quality and fix toxic links.
• BuzzSumo to uncover topics that resonate within your niche.
4. Content Quality Assessment
Content remains king. A detailed audit of your content ensures all pages deliver value and relevance.
5. User Experience (UX)
This should remove friction between completing a Task tightening engagement.